UNDERSTANDING DIABETES AND ITS COMPLICATIONS
What is Diabetes?
Types of Diabetes:
There are three main types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes.
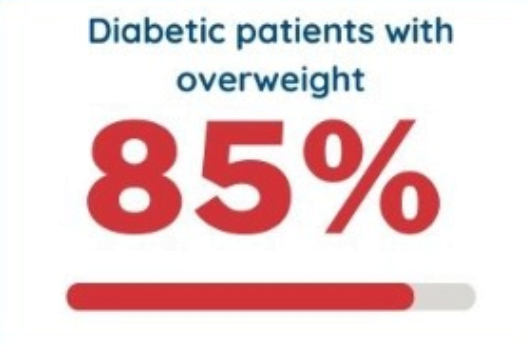
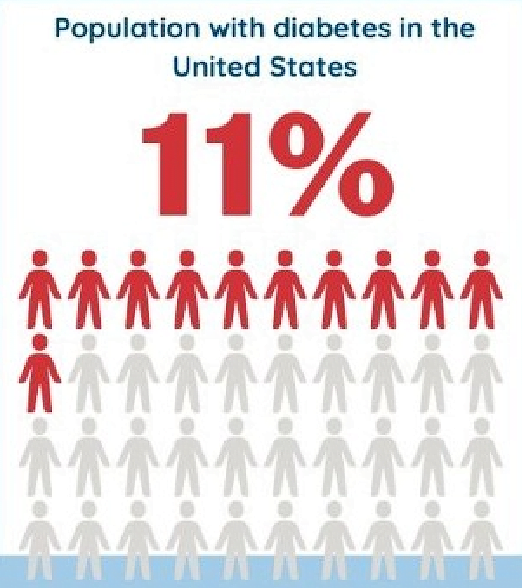
Diabetes Complications
Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to various complications that affect different parts of the body.
Cardiovascular Complications: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, including heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. Elevated blood sugar levels, combined with high blood pressure and cholesterol, can damage blood vessels and lead to these complications.
Neuropathy: Prolonged high blood sugar levels can damage the nerves throughout the body, most commonly affecting the feet and legs. Symptoms may include tingling, numbness, or pain in these areas. In severe cases, it can lead to foot ulcers or even amputation.
Retinopathy: Diabetes can damage the blood vessels in the retina, leading to diabetic retinopathy. It is a leading cause of blindness in adults. Regular eye examinations can help detect and manage this complication effectively.
Kidney Disease: High blood sugar levels over time can damage the kidneys, affecting their ability to filter waste from the blood. This condition, known as diabetic nephropathy, can progress to kidney failure, requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Other Complications: Diabetes can also affect other areas of the body, such as the skin, causing infections or slow-healing wounds. It can impact sexual health, leading to erectile dysfunction in men or sexual difficulties in women.
In conclusion :
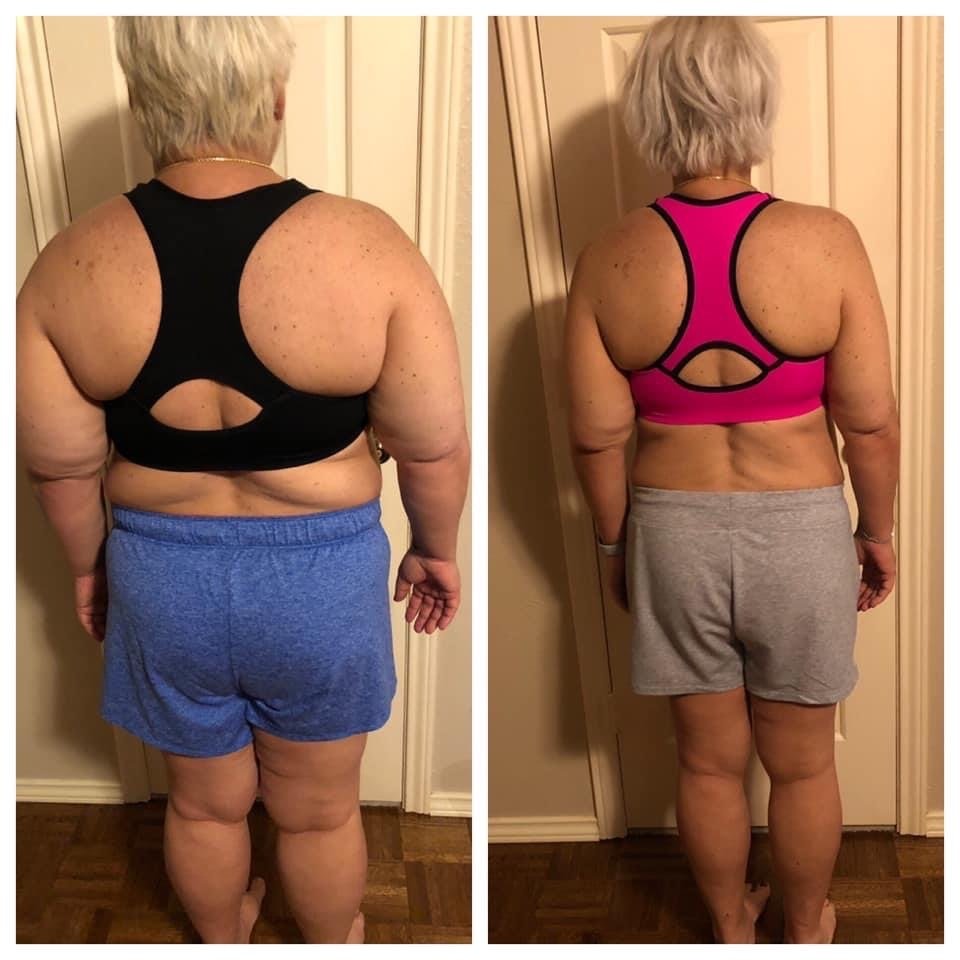
Before and After